Boiler safety is critical in maintaining a secure and efficient workplace, particularly in industries that rely on these powerful machines for daily operations.
Strict safety regulations are enforced in Canada, and ensuring that boilers operate safely is crucial to protecting employees and equipment.
Accidents involving boilers can lead to severe injuries, costly damages, and significant downtime, making safety a top priority.
In 2022, two Island Health workers were injured at Victoria General Hospital after a steam pipe exploded in the boiler, emphasizing the importance of boiler safety.
This article will provide a comprehensive boiler safety checklist to help you maintain safe operations and comply with Canadian safety standards.
We will cover essential aspects of boiler maintenance, including daily, weekly, monthly, and annual inspections and tasks.
By following this checklist, you can identify potential issues early, prevent accidents, and extend the lifespan of your boiler equipment.
This blog offers practical tips and guidelines that are easy to implement regardless of the size or type of your boiler.
Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to boiler operations, this checklist is designed to help you maintain a safe and efficient work environment.
The Boiler Safety Checklist
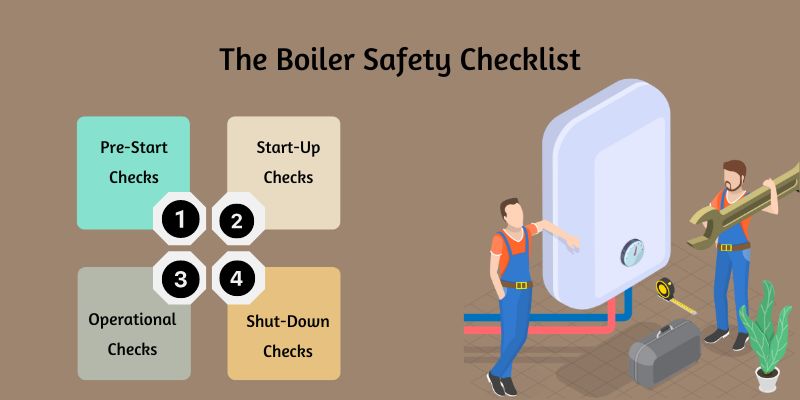
A comprehensive boiler safety checklist is essential for ensuring boiler systems' safe and efficient operation.
This checklist covers critical aspects of boiler maintenance, from pre-start checks to operational and shut-down procedures. It helps prevent accidents and prolong the life of the equipment.
1. Pre-Start Checks
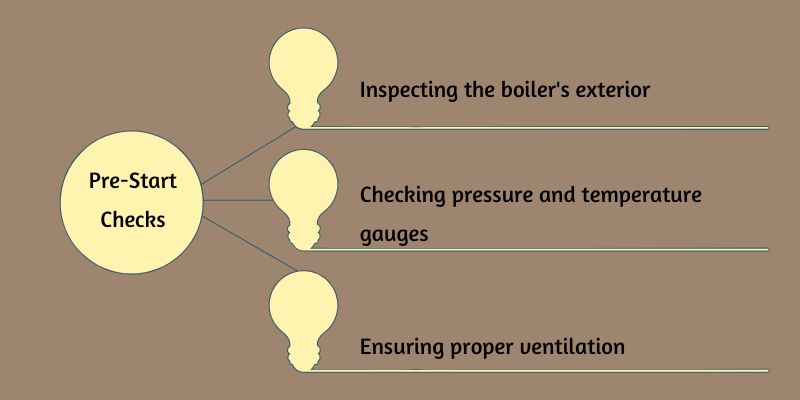
Perform a series of pre-start checks before starting a boiler to ensure that the system is safe to operate.
These checks can prevent potential hazards and ensure the boiler operates efficiently.
Inspecting the Boiler's Exterior
A thorough visual inspection of the boiler's exterior is the first step in the pre-start checklist.
Look for any signs of damage, such as dents, cracks, or corrosion, which could indicate underlying problems.
Ensure that all panels and doors are securely in place and that there are no visible leaks around seals and joints.
This inspection helps identify issues affecting the boiler's integrity or performance, allowing for timely repairs before they escalate into major problems.
Checking Pressure and Temperature Gauges
The next step is to check the pressure and temperature gauges. These gauges provide critical information about the boiler's operating conditions.
Ensure that the readings are within the manufacturer's recommended range. Abnormal readings can indicate issues such as overpressure, leading to dangerous situations.
Verify that safety valves are functioning correctly to prevent excessive pressure buildup.
Regularly calibrating these gauges ensures accurate readings and helps maintain safe operating conditions.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial for safe boiler operation. Check that the ventilation system is clear of obstructions and functioning correctly.
This includes ensuring that air intakes and exhaust outlets are debris-free and ventilation fans are operating efficiently.
Adequate ventilation prevents the buildup of harmful gases such as carbon monoxide, which can pose serious health risks to personnel.
Inadequate ventilation can also affect the boiler's combustion process, leading to inefficient operation and potential safety hazards.
By meticulously performing these pre-start checks, you can ensure that your boiler is in optimal condition before it begins operation.
This proactive approach to maintenance enhances safety and contributes to the longevity and efficiency of the boiler, ultimately safeguarding both your employees and your facility.
2. Start-Up Checks
After completing the pre-start checks, it's time for the start-up checks. These steps ensure that the boiler is prepared to operate safely and efficiently when turned on.
Verifying Water Levels
One of the most critical start-up checks is verifying the boiler's water levels. The water level in the boiler must be within the manufacturer's specified range to ensure proper operation.
Low water levels can lead to overheating and potential damage to the boiler, while high water levels can cause inefficient operation and water carryover into the steam system.
Use the sight glass or water level gauge to check the water level and ensure that automatic water feeders function correctly.
Monitoring water levels helps prevent dangerous conditions and maintains optimal boiler performance.
Checking Fuel Supply and Ignition Systems
Ensuring a reliable fuel supply and adequately functioning ignition systems is essential for safe boiler operation.
Inspect the fuel lines for leaks or obstructions and confirm the fuel pressure is within the recommended range.
Check the gas valve and burners for cleanliness and proper alignment for gas-fired boilers.
For oil-fired boilers, ensure the oil filters are clean and the fuel pump operates correctly. Test the ignition system to ensure that it lights smoothly and reliably.
A malfunctioning fuel supply or ignition system can lead to inefficient combustion, increased emissions, or even dangerous explosions.
Testing Safety Devices such as Relief Valves
Boiler safety devices, particularly relief valves, play a crucial role in preventing overpressure and ensuring the safe operation of the boiler.
During start-up checks, testing these devices to confirm they are working correctly is vital. Manually lift the test lever on the relief valve to ensure it opens and closes freely.
Additionally, check for any signs of corrosion or leakage around the valve.
Ensure all safety interlocks and boiler control systems, including low-water cutoffs and flame detectors, function correctly.
Regular testing and maintenance of these safety devices are essential to prevent dangerous pressure build-up and other hazardous conditions.
By performing these start-up checks, you ensure that the boiler is ready to operate and capable of doing so safely and efficiently.
These checks help identify and address potential issues before they can lead to significant problems, contributing to the overall safety and reliability of the boiler system.
3. Operational Checks
Once the boiler is up and running, it's crucial to perform ongoing operational checks to ensure it functions safely and efficiently.
These checks help detect any anomalies that could lead to more significant issues if left unattended.
Monitoring Pressure and Temperature
Consistently monitoring the pressure and temperature is vital for maintaining safe boiler operations.
Check the pressure gauge to ensure the boiler operates within the recommended pressure range specified by the manufacturer.
Any deviation from this range could indicate a problem with the boiler's pressure control system or a potential overpressure situation, which can be hazardous.
Similarly, monitor the temperature readings to ensure they remain within safe limits. Abnormally high temperatures can cause overheating, potentially leading to boiler failure.
Regularly recording these readings helps identify trends and spot issues early, allowing for prompt corrective actions.
Inspecting for Leaks or Unusual Noises
During operation, inspecting the boiler and its surroundings for any signs of leaks or unusual noises is essential.
Leaks can occur in various boiler system parts, including valves, pipes, and joints, leading to significant water loss, pressure drops, and potential damage to surrounding equipment.
Additionally, unusual noises such as banging, hissing, or whistling can indicate underlying issues such as trapped air, scale buildup, or mechanical problems within the boiler.
Addressing these signs promptly helps prevent minor issues from escalating into major, more costly repairs and ensures the boiler's safe operation.
Confirming Proper Functioning of Controls
The proper functioning of all control systems is essential for safe and efficient boiler operation. This includes checking the operation of thermostats, pressure controls, and safety shutoff devices.
Confirm that the control systems respond correctly to changes in operating conditions and maintain the desired pressure and temperature settings.
Verify that safety shut-offs and alarms function correctly to prevent the boiler from operating outside safe parameters.
Regularly testing these controls ensures that the boiler can safely adjust to varying conditions and that any faults in the control system are identified and corrected promptly.
By diligently performing these operational checks, you can ensure your boiler's ongoing safe and efficient performance.
Monitoring pressure and temperature, inspecting for leaks and unusual noises, and confirming the proper functioning of controls are all critical steps in maintaining the boiler system's reliability and longevity.
4. Shut-Down Checks
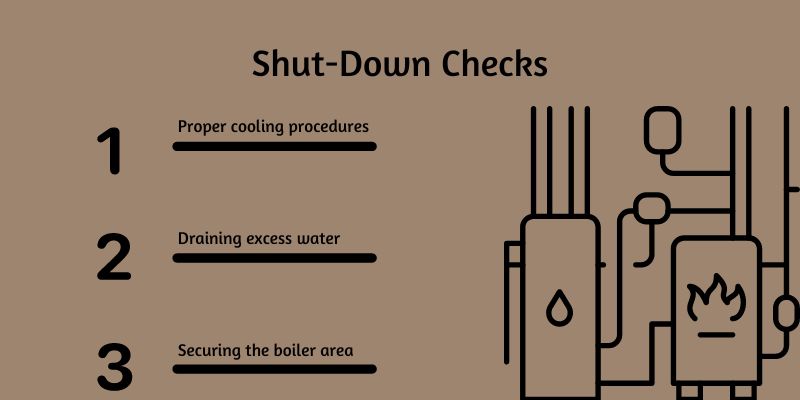
When it's time to shut down the boiler, performing thorough shut-down checks is essential to ensure the equipment is safely and effectively taken offline.
These checks help prevent damage during shut-down and prepare the boiler for its next start-up.
Proper Cooling Procedures
Proper cooling procedures are critical to safely shutting down a boiler. The boiler must be allowed to cool down gradually to prevent thermal stress and potential damage to the system.
Rapid cooling can cause the boiler's metal components to contract too quickly, leading to cracks or warping.
Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for cooling rates, and ensure that the boiler is brought down to a safe temperature before performing any further shut-down activities.
This controlled cooling process helps maintain the boiler's integrity and extends its lifespan.
Draining Excess Water
Draining excess water from the boiler is an essential step in the shut-down process, especially if the boiler will be out of service for an extended period.
Water left in the system can lead to corrosion and the buildup of sludge or scale, damaging the boiler and reducing efficiency.
Carefully drain the boiler according to the manufacturer's instructions, removing all water from the boiler and associated piping.
Properly draining the boiler prevents internal damage and prepares the system for maintenance or extended downtime.
Securing the Boiler Area
Securing the boiler area is crucial for safety during and after the shutdown process. Ensure that all energy sources, including electricity, gas, and steam, are safely isolated and locked out to prevent accidental reactivation.
Place appropriate signage around the boiler area to indicate that maintenance or shut-down procedures are in progress. Additionally, ensure that all access points to the boiler are secured to prevent unauthorized entry.
Securing the boiler area protects workers from accidental exposure to hazardous conditions. It ensures the boiler remains safe until it is ready to restart.
Following these shut-down checks, you can safely and effectively shut down your boiler.
Proper cooling procedures, draining excess water, and securing the boiler area are all essential steps to maintaining the safety and integrity of the boiler system.
4 Common Boiler Safety Issues and Solutions
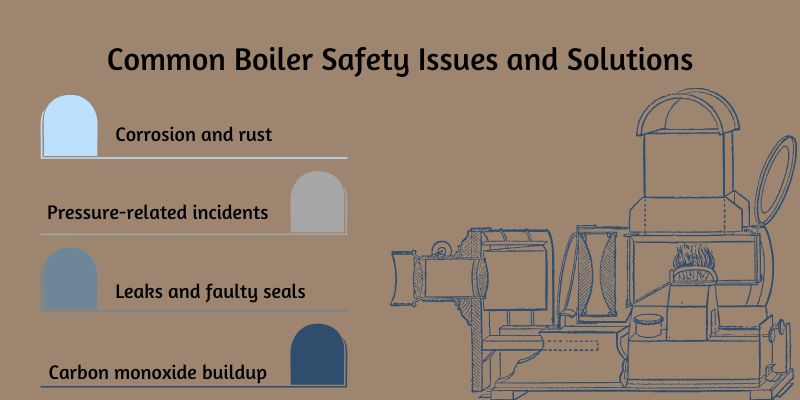
Boilers are essential components in many industries and buildings, providing heat and power. However, they can pose significant safety risks if not properly maintained and monitored.
Common safety issues such as corrosion, pressure-related incidents, leaks, and carbon monoxide buildup can lead to severe accidents, equipment damage, and even loss of life.
Understanding these issues and their solutions is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient boiler system.
1. Corrosion and Rust
Corrosion and rust are significant problems for boiler systems, primarily due to the presence of water and oxygen.
These elements react with metal surfaces, deteriorating the boiler's structural integrity over time. This can cause leaks, reduced efficiency, and potential boiler failure.
Solutions
-
Water Treatment: Implement a robust water treatment program to remove oxygen and other corrosive substances from the boiler water. Using chemical inhibitors can help prevent rust formation.
-
Regular Inspections: Inspect the boiler and its components for signs of corrosion and rust. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
-
Proper Maintenance: To minimize corrosive effects, maintain proper pH levels and control the concentration of dissolved solids in the boiler water.
2. Pressure-Related Incidents
Pressure-related incidents occur when the pressure inside the boiler exceeds safe levels, potentially leading to explosions or ruptures.
These incidents can result from malfunctioning pressure relief valves, blocked safety vents, or improper boiler operation.
Solutions
-
Pressure Relief Valves: Ensure that pressure relief valves are correctly installed, regularly tested, and maintained to function properly.
-
Monitoring Systems: Automate monitoring systems to continuously track boiler pressure and activate alarms if pressures exceed safe limits.
-
Operator Training: Train boiler operators on the correct procedures for maintaining and adjusting boiler pressure. Educate them on the signs of pressure issues and the appropriate responses.
3. Leaks and Faulty Seals
Leaks and faulty seals can occur in various boiler system parts, including pipes, valves, and joints.
These leaks not only reduce efficiency but can also pose safety hazards due to potential exposure to hot steam or water.
Solutions
-
Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance checks on all boiler components, focusing on seals, gaskets, and joints to ensure they are intact and functioning correctly.
-
Prompt Repairs: Immediately address detected leaks to prevent further damage and maintain system integrity.
-
Quality Parts: Use high-quality, compatible parts for repairs and replacements to ensure long-lasting and reliable seals.
4. Carbon Monoxide Buildup
Carbon monoxide buildup is a critical safety issue, as this odorless, colorless gas can cause severe health problems or even death.
Buildups typically occur due to incomplete combustion of fuel or inadequate ventilation.
Solutions
-
Proper Ventilation: Ensure that the boiler room has adequate ventilation to allow for the proper expulsion of gases. Regularly check and maintain ventilation systems.
-
Combustion Efficiency: Regularly service and tune the boiler to ensure complete fuel combustion, which minimizes carbon monoxide production.
-
CO Detectors: Install carbon monoxide detectors in and around the boiler room. These detectors can warn about dangerous CO levels early, allowing for timely evacuation and corrective measures.
By understanding these common boiler safety issues and implementing practical solutions, you can significantly reduce the risks associated with boiler operation.
Regular maintenance, proper training, and appropriate safety measures are crucial to ensuring a safe and efficient boiler system.
Training and Education
Training and education are fundamental components of ensuring boiler safety and efficiency. Well-informed boiler operators are crucial for maintaining safe operations and preventing accidents.
Comprehensive training programs and continuous education help operators stay current with the latest safety standards and technological advancements.
Importance of Proper Training for Boiler Operators
Proper training for boiler operators is crucial to ensure boiler systems' safe and efficient operation.
Boilers are complex equipment that requires skilled handling to prevent accidents, equipment damage, and operational inefficiencies. Here's why proper training is so essential:
Safety and Compliance
-
Preventing Accidents: Properly trained operators are well-versed in safety protocols and procedures, significantly reducing the risk of accidents. They can identify potential hazards and take corrective actions before they escalate into serious incidents.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Many regions, including Canada, have strict boiler operation regulations. Training ensures that operators are familiar with these regulations and can operate the boiler in compliance with legal standards, avoiding fines and shutdowns.
Efficient Operation
-
Optimal Performance: Trained operators understand how to run the boiler efficiently, which helps maintain optimal performance. This includes managing fuel consumption, maintaining appropriate pressure and temperature levels, and conducting routine checks and maintenance. WHMIS training online equips operators with the necessary knowledge to safely handle hazardous materials and maintain a safe working environment.
-
Cost Savings: Efficient operation leads to cost savings by reducing fuel consumption and minimizing wear and tear on the equipment. Properly trained operators can also identify and address minor issues before they become costly repairs.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
-
Routine Maintenance: Training equips operators with the knowledge to perform routine maintenance tasks. Regular maintenance is crucial for prolonging the boiler's lifespan and preventing breakdowns.
-
Effective Troubleshooting: When issues arise, trained operators can troubleshoot and resolve problems quickly and effectively, minimizing downtime and maintaining the boiler system's reliability.
Environmental Impact
- Reducing Emissions: Well-trained operators can ensure the boiler operates within environmental regulations, minimizing harmful emissions. This is particularly important in industries where boilers are a significant source of greenhouse gases.
- Energy Efficiency: Training focuses on energy-efficient practices, which help reduce the boiler operation's overall environmental footprint.
Professional Development
-
Skill Enhancement: Ongoing training and education help operators keep up with technological advancements and new best practices in boiler operation. This continuous learning process enhances their skills and career prospects.
-
Certification: Many training programs offer certification, which validates the operator's skills and boosts their professional credibility and job security.
Steps to Ensure Proper Training
-
Accredited Programs: Enroll operators in accredited training programs covering theoretical and practical knowledge.
-
On-the-Job Training: Provide hands-on training under the supervision of experienced professionals to reinforce classroom learning.
-
Regular Refresher Courses: Organize regular refresher courses to keep operators updated on the latest safety protocols, technologies, and regulatory changes.
-
Simulation Exercises: Use simulation exercises to practice handling emergencies in a controlled environment.
-
Continuous Assessment: Implement continuous assessment and feedback mechanisms to ensure operators maintain high competency standards.
Proper boiler operator training is not just a regulatory requirement but a vital aspect of ensuring boiler systems' safety, efficiency, and longevity. Investing in comprehensive training programs ultimately benefits the organization through improved safety records, operational efficiency, and cost savings.
Conclusion
Ensuring the safe and efficient operation of boilers is paramount in any industry relying on these systems.
This comprehensive boiler safety checklist highlights the critical areas that need regular attention to prevent accidents, maintain operational efficiency, and comply with regulatory standards.
From pre-start checks to post-shutdown procedures, every step is designed to identify potential hazards, rectify issues promptly, and ensure that the boiler operates within safe parameters.
One of the key takeaways from this guide is the importance of a systematic approach to boiler maintenance.
Regular inspections and maintenance not only prevent accidents but also extend the lifespan of your boiler, leading to significant cost savings in the long run.
Adhering to a detailed boiler safety checklist and prioritizing operator training are essential components of a robust boiler safety program.
These practices help mitigate risks, enhance efficiency, and ensure compliance with safety standards, ultimately protecting both the workforce and the facility.
Regularly revisiting and updating your safety protocols in light of new technologies and regulations will strengthen your commitment to maintaining a safe and efficient boiler system.