Cognitive distraction is the mental diversion that occurs when our focus is shifted from the task, often leading to errors and accidents.
Understanding cognitive distraction is crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency in various aspects of life, especially in activities that demand high concentration levels, such as driving or operating machinery.
Cognitive distraction while driving is particularly hazardous. Activities such as talking on the phone or daydreaming can divert a driver's attention from the road, significantly increasing the risk of road accidents.
When drivers are not entirely focused on driving, they are more likely to make critical errors that can lead to collisions, injuries, and fatalities. This lack of focus endangers the driver and seriously threatens passengers, pedestrians, and other road users.
Transport Canada's National Collision Database data shows that distracted driving contributed to an estimated 22.5% of fatal collisions and 25.5% of serious injury collisions in 2021.
This blog will explore the importance of recognizing cognitive distractions while driving, explaining their dangers, and providing practical tips for staying focused.
Understanding and addressing cognitive distractions can improve our focus, enhance road safety, and lead more productive and fulfilling lives.
Definition of Cognitive Distraction

Cognitive distraction is any mental activity or thought process that diverts an individual's attention from the primary task.
Unlike physical distractions, which involve external stimuli that can be seen or heard, cognitive distractions occur internally within the mind.
These distractions can significantly impair one's ability to focus, make decisions, and perform tasks efficiently and safely.
Cognitive distractions can manifest in various forms, including daydreaming, preoccupation with personal issues, stress, fatigue, and even multitasking.
When a person's mind is engaged in unrelated thoughts, it reduces the mental resources available for the primary task, leading to errors, decreased productivity, and, in some cases, safety risks.
Types of Cognitive Distractions

Cognitive distractions are mental distractions that divert our attention from the task. They come in various forms and can significantly impact our productivity, safety, and well-being.
Understanding the different types of cognitive distractions is crucial for developing strategies to manage them effectively. Here, we will explore the primary types of cognitive distractions in detail.
Internal Distractions
-
Thoughts and Worries: Internal distractions often stem from our thoughts and worries. Personal concerns, such as family issues, financial problems, or health worries, can occupy our minds and prevent us from focusing on our tasks. Our attention is divided when we are preoccupied with these thoughts, making concentrating difficult.
-
Daydreaming: Daydreaming is another common internal distraction where the mind wanders to thoughts unrelated to the current activity. While daydreaming can sometimes lead to creative insights, it often disrupts our ability to stay engaged with the task at hand, reducing productivity and efficiency.
-
Fatigue and Stress: Mental fatigue and stress can also lead to internal distractions. When we are tired or stressed, our cognitive resources are depleted, making it harder to maintain focus. This can result in frequent mind-wandering and difficulty in staying attentive.
External Distractions
-
Environmental Noise: External distractions come from our surroundings. Environmental noise, such as conversations, traffic, or construction sounds, can easily divert our attention. Open office layouts can be particularly challenging in a workplace setting, as constant noise and interruptions can significantly reduce productivity.
-
Visual Distractions: Visual distractions, such as movement or clutter in the workspace, can distract our attention from our tasks. For instance, having a television in the background or notifications on a screen can interrupt our concentration.
-
Interruptions from Others: Interruptions from colleagues, phone calls, or emails are common external distractions in professional and personal settings. These interruptions can break our focus and make it challenging to resume our tasks, leading to decreased efficiency.
Multitasking
-
Switching Tasks: Multitasking is often perceived as a way to increase productivity, but it divides our attention and reduces the quality of our work. Switching between tasks requires cognitive effort to reorient ourselves, leading to mental fatigue and errors. For example, checking emails while working on a report can result in mistakes in both tasks.
-
Competing Priorities: When we try to juggle multiple responsibilities or projects simultaneously, giving each task the attention it deserves can be challenging. This can lead to incomplete or poorly executed tasks, as our cognitive resources are spread too thin.
Technological Distractions
-
Smartphones and Social Media: In the digital age, technological distractions are pervasive. Smartphones and social media are significant sources of cognitive distraction. The constant notifications, messages, and social media updates can distract us from our tasks, making it difficult to focus.
-
Email and Instant Messaging: Email and instant messaging platforms are essential tools for communication, but they can also be significant distractions. The urge to immediately check and respond to messages can interrupt our workflow and decrease productivity.
-
Digital Multitasking: Engaging in multiple digital activities simultaneously, such as watching videos while browsing the internet or working on multiple devices, can overload our cognitive capacity. This can lead to decreased attention span and increased errors.
Emotional Distractions
-
Emotional Reactions: Emotional distractions occur when strong emotions, such as anger, sadness, or excitement, capture our attention. Personal experiences, interactions with others, or external events can trigger these emotions. When we are emotionally distracted, it is difficult to concentrate on tasks and make rational decisions.
-
Relationship Issues: Conflicts or concerns related to personal or professional relationships can also be a significant source of emotional distraction. Worrying about a disagreement with a colleague or issues at home can consume our mental energy and reduce our ability to focus on work.
Physical Distractions
-
Physical Comfort: Physical discomfort, such as being too hot or cold or experiencing pain, can be a distraction. Ensuring a comfortable working environment can minimize these distractions and improve focus.
-
Hunger and Thirst: Basic physical needs, such as hunger and thirst, can also be distracting. However, caring for these needs is essential to maintaining optimal cognitive function.
Cognitive distractions come in many forms, potentially disrupting our focus and productivity.
By understanding the various cognitive distractions—internal, external, multitasking, technological, emotional, and physical—we can develop strategies to mitigate their impact.
Techniques such as mindfulness, creating a conducive work environment, setting boundaries for technology use, and addressing emotional and physical needs can help manage distractions and improve our ability to concentrate on essential tasks.
Recognizing and addressing cognitive distractions is essential for enhancing performance and well-being in both personal and professional life.
Effects of Cognitive Distraction
Cognitive distraction is a mental state in which a person's attention is diverted from the task by engaging in unrelated thoughts or activities.
This phenomenon has far-reaching effects on various aspects of our lives, significantly impacting our daily tasks, productivity, decision-making abilities, learning, memory retention, and mental health.
Understanding these effects is crucial to managing and mitigating the negative impacts of cognitive distractions.
1. Impacts on Daily Tasks and Productivity
Cognitive distractions can hinder our ability to complete daily tasks efficiently and effectively.
When our minds wander or are preoccupied with unrelated thoughts, we become less attentive to the task, which can lead to mistakes and decreased productivity.
For example, employees distracted by personal concerns or external stimuli may need help focusing on their work in a workplace setting, which can result in errors, missed deadlines, and lower overall output.
Furthermore, multitasking, often seen as a productivity booster, is a form of cognitive distraction. Switching between tasks can fragment our attention, making it harder to complete each task with the required precision and speed.
Research has shown that it takes the brain a significant amount of time to refocus after a distraction, cumulatively leading to a substantial loss in productivity.
Cognitive distractions can also interfere with routine activities such as driving, cooking, or even conversing with others daily.
A distracted driver, for instance, is at a higher risk of accidents as they might miss crucial traffic signals or react slower to sudden changes in road conditions.
Similarly, distractions while cooking can lead to burnt meals or kitchen accidents, and not paying full attention during conversations can cause misunderstandings and strained relationships.
2. Influence on Decision-Making and Problem-Solving Abilities
Effective decision-making and problem-solving require a clear, focused mind. Cognitive distractions impair these critical thinking processes by overwhelming our mental resources with irrelevant information.
When distracted, we are more likely to make impulsive decisions rather than well-thought-out ones, as our ability to weigh options and consider potential outcomes is compromised.
For example, in a business context, a manager preoccupied with unrelated thoughts may need to pay attention to critical data or consider all aspects of a decision, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
In personal life, distractions can lead to poor financial decisions, such as impulse purchases, because they reduce the cognitive effort required to deliberate and evaluate choices.
Moreover, problem-solving often requires creative thinking and connecting disparate pieces of information.
Cognitive distractions can stifle creativity by preventing the mind from engaging deeply with the problem. When distractions occupy our mental bandwidth, we are less likely to generate innovative solutions or think outside the box.
3. Consequences for Learning and Memory Retention
Cognitive distractions significantly affect our ability to learn and retain information. Effective learning requires sustained attention and engagement with the material.
Distractions disrupt this process by breaking our focus, making it harder to absorb and understand new information.
Students distracted by thoughts unrelated to their studies, such as social media or personal worries, are less likely to perform well academically in educational settings.
They may miss critical points during lectures, fail to complete assignments accurately, and need help recalling information during exams. These issues affect not only their grades but also their overall educational experience.
Cognitive distractions similarly impact memory retention. Forming long-term memories involves consolidating information, which requires undivided attention.
This consolidation process is interrupted when distracted, leading to poor memory formation and recall.
For instance, someone trying to remember a list of items while their mind is wandering will likely forget some of the items. This can have practical implications, such as forgetting necessary appointments or tasks.
4. Relationship Between Cognitive Distraction and Stress/Anxiety
Cognitive distractions can also contribute to increased stress and anxiety. Constantly pulling our minds in different directions can create a sense of mental overload and chaos.
This perpetual state of distraction prevents us from fully engaging in any one activity, leading to feelings of frustration and inadequacy.
For example, employees who are constantly distracted at work may feel stressed about their inability to meet deadlines or perform at the highest level.
This stress can further exacerbate their distractibility, creating a vicious cycle of decreased productivity and increased anxiety.
Additionally, cognitive distractions can interfere with relaxation and leisure activities, preventing us from fully unwinding and recharging, which is essential for mental health.
Moreover, being distracted can heighten our sensitivity to stressors. Even minor inconveniences can feel overwhelming when we are not fully present, leading to heightened stress levels.
Over time, chronic stress can contribute to anxiety disorders, as the mind struggles to cope with the constant barrage of distractions and demands.
Cognitive distractions profoundly affect our daily tasks, productivity, decision-making, learning, memory retention, and mental health. Recognizing managing these distractions is crucial for improving our focus, efficiency, and overall well-being.
By implementing strategies to minimize distractions, such as practicing mindfulness, setting clear priorities, and creating conducive work environments, we can better navigate modern life's demands and achieve tremendous success in our personal and professional endeavors.
4 Strategies to Manage Cognitive Distraction
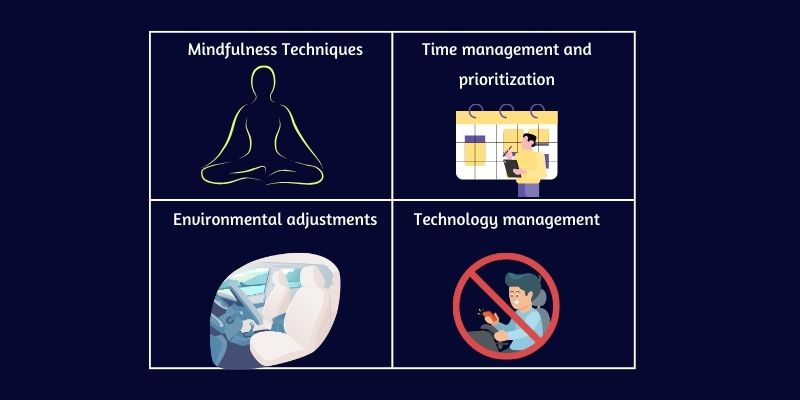
Cognitive distractions can significantly impact productivity, safety, and overall well-being.
Managing these distractions involves implementing effective strategies that help individuals stay focused and improve their cognitive performance while driving.
Below are some detailed approaches to managing cognitive distractions.
1. Mindfulness Techniques
Mindfulness involves being fully present and engaged in the moment, which can reduce the impact of cognitive distractions.
Meditation
-
Daily Practice: Regular meditation helps calm the mind and improve focus. Practices like deep breathing, guided visualization, or sitting in silence can significantly reduce mental clutter.
-
Mindful Breathing: Taking a few moments throughout the day to focus on breathing can help center the mind and bring attention back to driving.
Mindful Awareness
-
Staying Present: Actively focusing on driving and acknowledging when the mind starts to wander can improve concentration. Techniques like mentally noting "wandering" and gently bringing attention back can be effective.
-
Sensory Engagement: Engaging the senses by noting what you see, hear, smell, taste, and feel helps anchor your awareness in the present moment, reducing internal distractions.
Mindful Breaks
-
Short Breaks: Regular breaks to practice mindfulness can refresh the mind. Step away from work during these breaks and stretch, walk, or observe your surroundings.
Driver fatigue is also the leading cause of cognitive distraction, and the only solution to this problem is to implement defensive driving techniques effectively.
We recommend an Online Defensive Driving Course by the Canada Safety Training Centre to explore the examples and understand the benefits of defensive driving. It can help you with the skills needed to become a better driver.
2. Time Management and Prioritization
Effective time management and prioritization can help manage cognitive distractions by creating a structured and focused work environment.
Task Lists
-
Daily Planning: Creating a list of tasks for the day helps prioritize important activities and reduces the cognitive load of remembering everything. Using tools like to-do lists or digital planners can be helpful.
-
Prioritization: Ranking tasks by importance and urgency ensures that critical tasks are addressed first, preventing the mind from worrying about pending activities.
Time Blocking
-
Scheduled Focus: Allocating specific time blocks for different tasks helps concentrate effort and reduce multitasking. During these blocks, avoid engaging in unrelated activities.
-
Breaks and Downtime: Scheduling regular breaks prevents burnout and maintains cognitive efficiency. Breaks can be used for relaxation or mindfulness exercises.
Avoiding Multitasking
-
Single-tasking: Focusing on one task at a time improves quality and reduces mental fatigue. Multitasking can divide attention and increase cognitive load.
-
Batch Processing: Grouping similar tasks can streamline processes and reduce the frequency of switching between different activities.
3. Environmental Adjustments
Creating a conducive environment can minimize external distractions and enhance focus.
Organized Space
-
Decluttering: Keeping your car clean and organized reduces visual distractions and creates a more productive environment.
-
Ergonomic Setup: Ensuring the car is comfortable and has proper lighting, seating, and equipment placement can reduce physical discomfort and distractions.
Noise Control
-
Quiet Spaces: Working in quiet areas or using noise-canceling headphones can minimize auditory distractions.
-
White Noise: Some individuals find that white noise or background music helps maintain focus by drowning out disruptive sounds.
Visual Cues
-
Focused Space: Creating a workspace with minimal visual distractions helps maintain attention on the task.
4. Technology Management
Managing technology effectively is crucial in minimizing digital distractions while driving.
Notification Management
-
Disabling Notifications: Turning off non-essential notifications on phones and computers reduces interruptions.
-
Scheduled Check-ins: Setting specific times to check emails and messages rather than responding immediately can improve focus.
Digital Tools
-
Focus Modes: Activating focus modes on devices during work periods can reduce digital interruptions.
Digital Detox
-
Tech-Free Time: Allocating certain periods of the day or specific days for a digital detox can refresh the mind and reduce reliance on constant connectivity.
-
Mindful Technology Use: Being intentional about when and how technology is used helps in reducing its distracting impact.
Individuals can significantly reduce cognitive distractions by incorporating mindfulness techniques, effective time management, creating a conducive work environment, and managing technology wisely.
These strategies enhance productivity and focus and contribute to well-being and mental clarity.
Cognitive Distraction - FAQs
How does cognitive distraction affect our ability to focus and concentrate?
Cognitive distraction diverts attention from the primary task, reducing focus and concentration, leading to mistakes and decreased productivity.
What does cognitive mean in driving?
Cognitive refers to the mental processes involved in driving, such as attention, decision-making, and reaction time, all of which can be impaired by distractions.
What causes cognitive distractions?
Cognitive distractions are caused by engaging in activities that divert attention from the primary task, such as thinking about personal issues, multitasking, or using electronic devices.
Final words
Managing cognitive distraction while driving is essential for driving on a highway or at night.
Mindfulness techniques can help maintain focus and reduce mental clutter, while effective time management and prioritization ensure you can drive safely.
Creating an organized and distraction-free environment and managing technology can enhance our ability to enjoy a safe ride.
Whether turning off non-essential notifications, using productivity apps, or scheduling regular breaks, these practices collectively contribute to a more structured and less distracted journey.
Addressing cognitive distractions requires a proactive approach so individuals can maintain concentration while ascertaining the safety of other passengers and pedestrians.