Workplace lubricants, ranging from oils to greases, are essential in machinery and equipment maintenance, ensuring smooth operations and longevity.
Understanding the significance of workplace lubricants is the first step in appreciating their role. These substances are designed to reduce friction, prevent wear and tear, and enhance the overall efficiency of machinery.
While they are indispensable, it's crucial to acknowledge that mishandling or neglecting workplace lubricant safety precautions can pose severe risks to personnel and the workplace.
Safety precautions are vital to safeguarding employees and maintaining a secure work environment. This blog will explore various safety measures, from proper storage and handling practices to using personal protective equipment (PPE).
We'll address potential hazards associated with workplace lubricants and provide actionable insights to mitigate risks effectively.
Whether you are a seasoned professional working with lubricants daily or someone new to the field, our guide aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to prioritize safety.
By adopting these precautions, workplaces can ensure the well-being of their employees and the seamless functioning of machinery, contributing to a safer and more productive work environment.
Join us as we navigate the essential safety precautions crucial for anyone dealing with workplace lubricants.
Potential Hazards of Workplace Lubricants

From health risks involving inhalation and skin contact to the intricacies of fire and explosion hazards, here are some potential hazards of workplace lubricants.
Health Hazards of Workplace Lubricants
While essential for machinery function, workplace lubricants can pose health hazards to employees without proper precautions.
Understanding and mitigating health risks associated with these substances is vital for maintaining a safe work environment.
Inhalation Risks
Inhalation hazards arise when employees are exposed to lubricant vapors, mists, or aerosols. Specific lubricants may contain volatile components that, when evaporated, can be inhaled by workers.
Prolonged exposure to these substances can lead to respiratory issues, irritation of the respiratory tract, and, in extreme cases, more severe health effects.
Mitigation Strategies
-
Ventilation Systems: Adequate workplace ventilation systems can help disperse vapors and maintain air quality.
-
Respiratory Protection: Depending on the type of lubricant and the potential for inhalation exposure, providing employees with appropriate respiratory protective equipment is crucial.
Skin Contact Risks
Lubricants often contain chemicals that can be absorbed through the skin, leading to various adverse effects. Prolonged or repeated skin contact may cause irritation, dermatitis, or more severe health issues.
Skin absorption is a significant concern, especially when handling lubricants without suitable personal protective equipment (PPE).
Mitigation Strategies
-
Use of PPE: Providing employees with protective clothing, including gloves and aprons, helps minimize direct skin contact.
-
Handwashing and Hygiene Practices: Encouraging regular handwashing and maintaining good hygiene practices can reduce the risk of skin absorption.
Eye Contact Risks
Lubricants can threaten eye health if there is accidental splashing or contact. Chemicals in specific lubricants may cause irritation, redness, or more severe eye injuries.
Mitigation Strategies
-
Eye Protection: Wearing safety goggles or face shields can protect the eyes from potential splashes or contact.
- Implementing these mitigation strategies is crucial for safeguarding the health of employees working with lubricants.
Organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with inhalation, skin contact, and eye exposure to workplace lubricants by promoting awareness, providing appropriate PPE, and ensuring adherence to safety protocols.
Fire and Explosion Risks of Workplace Lubricants
Workplace lubricants introduce potential fire and explosion risks, emphasizing the need for strict safety measures to prevent such hazards.
Understanding the combustibility of lubricants and identifying potential ignition sources are crucial components of a comprehensive safety approach.
Combustibility of Lubricants
Lubricants, especially those derived from petroleum-based sources, may possess flammable properties. These substances can ignite and sustain combustion under specific conditions, such as exposure to high temperatures, sparks, or open flames.
The volatility of specific lubricants increases the likelihood of fire hazards, particularly in environments where machinery operates at elevated temperatures.
Mitigation Strategies
-
Material Selection: Choosing lubricants with lower flammability characteristics can reduce the risk of combustion.
-
Temperature Control: Implementing measures to control machinery temperatures can minimize the likelihood of lubricant ignition.
Ignition Sources
Identifying and managing potential ignition sources is crucial for preventing workplace fires. Ignition sources range from electrical equipment and machinery sparks to hot surfaces near lubricant use.
Any source capable of igniting the lubricant vapors or substances should be carefully managed to avoid fire incidents.
Mitigation Strategies
-
Isolation of Ignition Sources: Ensuring that machinery and equipment prone to sparks or high temperatures are isolated from lubricant storage or application areas.
-
Regular Inspections: Conducting regular inspections to identify and address potential ignition sources in the workplace.
Effectively managing fire and explosion risks associated with workplace lubricants involves a combination of preventive measures, employee training, and ongoing assessments.
Organizations should implement comprehensive safety protocols, including proper material selection, temperature control, and identifying and isolating potential ignition sources, to minimize the risk of incidents and create a safer work environment.
Workplace Lubricant Safety Precautions
Implementing safety precautions when dealing with workplace lubricants is vital to protect employees and maintain a secure working environment.
Several key safety measures, ranging from personal protective equipment (PPE) to proper storage and handling, contribute to minimizing risks associated with lubricant usage.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
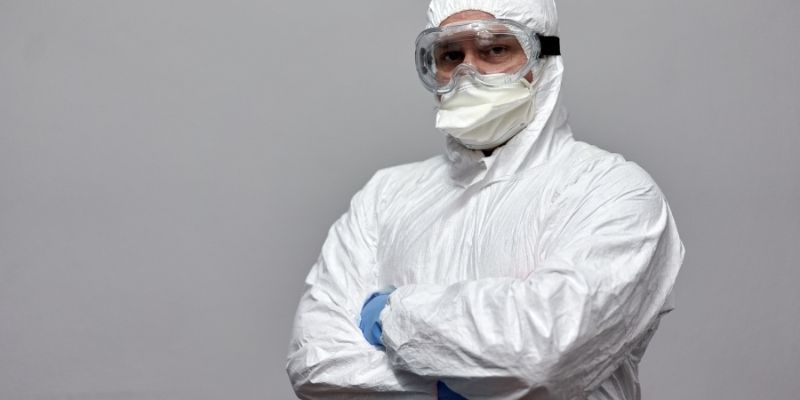

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is crucial to workplace lubricant safety, protecting against potential hazards. Here's a detailed explanation of each element:
Gloves
Wearing appropriate gloves is a fundamental aspect of workplace lubricant safety. Different lubricants may contain substances that can be absorbed through the skin, leading to potential health hazards.
Providing chemical-resistant gloves suitable for the specific lubricant creates a barrier between the skin and the lubricant. This prevents direct contact, reducing the risk of skin irritation, dermatitis, or absorption of harmful substances.
Employees handling lubricants should be trained on the selection and proper use of gloves, emphasizing the importance of changing them regularly to maintain their effectiveness.
Eye Protection
Eye protection is essential to shield workers from potential splashes or accidental contact with lubricants that could cause eye irritation or more severe injuries.
Safety goggles or glasses designed to resist chemical exposure should be worn in areas where there is a risk of eye contact with lubricants. Proper eye protection safeguards against immediate injury and helps prevent long-term eye damage due to repeated exposure.
Respirators
In work environments with inhalation risks associated with lubricants, respirators become crucial. Respirators help protect employees from inhaling vapors, fumes, or aerosols that may pose respiratory hazards.
The appropriate respirator selection depends on the type and concentration of contaminants present. Regular training on the correct use, maintenance, and storage of respirators is essential to ensure their effectiveness and the safety of workers.
Implementing proper personal protective equipment is a foundational step in minimizing the health risks associated with workplace lubricants. It protects individual employees from potential harm and creates a safer and more secure work environment overall.
Regular PPE training sessions and updates on PPE usage ensure that employees remain well-informed and equipped to handle lubricants safely.
2. Proper Storage and Handling
Handling and adequately storing the lubricants is essential for the safety of personnel. Here are some main complaints that can ascertain proper storage and handling.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage of workplace lubricants is critical to ensuring both the longevity of the lubricants and the safety of employees.
Lubricants should be stored in designated areas that are well-ventilated, dry, and away from direct sunlight.
Containers or drums holding lubricants should be labeled with relevant information, including the type of lubricant, potential hazards, and proper handling instructions.
Following storage guidelines helps prevent contamination, degradation, or spillage, maintaining the integrity of the lubricants.
Handling Procedures
Safe handling procedures are essential to minimize the risks associated with workplace lubricants.
Employees should be trained on the correct methods for transporting, dispensing, and applying lubricants. This includes using appropriate tools and equipment to prevent spills or leaks.
Handling procedures also involve ensuring that containers are tightly sealed when not in use to avoid exposure to air and contaminants.
Spill response plans should be in place, outlining the steps to be taken in the event of a spill or leak. This includes readily available absorbent materials, containment measures, and proper disposal methods.
Employees should understand the importance of promptly reporting spills or leaks to the designated personnel to ensure swift and effective response.
Regular inspections of storage areas and handling equipment contribute to identifying potential issues before they escalate.
Training programs should emphasize the significance of adhering to established storage guidelines and handling procedures, as outlined in WHMIS certificate, to maintain a safe working environment.
Compliance with these guidelines not only safeguards the health and well-being of employees but also prevents environmental contamination and contributes to overall workplace safety.
3. Employee Training
Employee training is crucial in improving workers' understanding of lubricant hazards.
Understanding Lubricant Hazards
Comprehensive employee training is indispensable for ensuring workplace safety when dealing with lubricants.
Training programs should focus on enhancing employees' understanding of the potential hazards of various lubricants. This includes educating them about the specific health risks related to inhalation, skin contact, or ingestion of these substances.
Employees must be familiar with the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) or Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for each lubricant used in the workplace.
These documents provide crucial information about the properties, hazards, and safe handling practices of the respective lubricants.
Employees should be trained to recognize warning signs and labels on lubricant containers, indicating potential dangers and preventive measures.
Canada Safety Training offers some of the most comprehensive training programs. Here are some of them:
-
Fire Extinguisher Training
-
Hazard Recognition Training
-
Accident and Incident Investigation Training
-
Confined Space Awareness Training
-
Lockout Tagout Training
-
H2S Training Course
-
PPE Training
Understanding the properties of lubricants, such as flammability or toxicity, empowers workers to make informed decisions and take necessary precautions during storage, handling, and application.
Emergency Response Training
In addition to understanding hazards, employees should undergo specialized emergency response training. This training equips them with the knowledge and skills required to respond effectively in case of accidents, spills, leaks, or other lubricant-related emergencies.
Employees must be familiar with the location and proper usage of emergency equipment, such as eye wash stations, safety showers, fire extinguishers, and spill response kits.
Emergency response training should encompass protocols for notifying supervisors or designated personnel, evacuating the area when necessary, and providing first aid in case of injuries.
Regular emergency drills reinforce these procedures, ensuring employees are well-prepared to handle unexpected situations involving lubricants.
The goal is to create a proactive safety culture where employees are aware of potential hazards and trained to respond swiftly and effectively to mitigate risks and protect themselves and their colleagues.
4. Ventilation Systems

Proper ventilation is a critical component of workplace safety when dealing with lubricants. Ventilation systems play a pivotal role in maintaining air quality by removing potentially harmful fumes, vapors, or airborne particles generated during the use or application of lubricants.
These systems are designed to control and reduce exposure levels, creating a healthier and safer environment for employees.
The primary goal of ventilation is to prevent the accumulation of hazardous substances in the air, ensuring that concentrations remain below permissible exposure limits (PELs) or other established workplace exposure standards.
Adequate ventilation is particularly crucial in enclosed or confined spaces where the dispersal of fumes may be limited.
Installation and Maintenance
Properly installing and regularly maintaining ventilation systems are paramount to their effectiveness.
Installation should be carried out by qualified professionals following industry standards and guidelines.
The design of the ventilation system should consider the specific characteristics of the workplace, including the types of lubricants used, the size of the area, and the nature of the tasks performed.
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure that ventilation systems operate efficiently over time. This includes inspecting and cleaning components such as ducts, filters, fans, and exhaust outlets.
Any malfunction or degradation of the system should be promptly addressed to prevent compromised air quality.
Employers must establish a routine schedule for ventilation system inspections and maintenance, and employees should be trained to recognize signs of system issues.
This proactive approach not only safeguards the health and well-being of workers but also contributes to a safer work environment by minimizing the potential risks associated with exposure to lubricant-related contaminants.
5. Emergency Response Procedures
When it comes to controlling hazardous situations, effective and practical emergency response procedures set the tone for the control attempts.
It provides guidelines for the employees to follow for incident control and management.
Spill Response
In a lubricant spill, immediate and effective actions are crucial to minimize hazards and prevent further environmental impact.
Employees should be trained on the proper spill response procedures, including using spill kits and personal protective equipment (PPE). Immediate actions may involve:
-
Containing the spill.
-
Using absorbent materials to limit its spread.
-
Notifying designated personnel responsible for cleanup.
Cleanup procedures must be well-defined, specifying the appropriate methods and materials for safely and efficiently addressing spills. This may include the use of absorbents, containment booms, or vacuum systems, depending on the nature and size of the spill.
Proper disposal of contaminated materials is integral to the cleanup process to mitigate environmental risks.
Fire Response
Lubricants pose a risk of fire and combustion, especially in the presence of ignition sources. Employees must be trained on fire response procedures to ensure a swift and organized reaction in case of fire emergencies.
This includes understanding how to use fire extinguishers and knowing the location of emergency exits and evacuation routes.
The effective use of fire extinguishers involves the PASS technique:
-
Pull the pin
-
Aim the nozzle
-
Squeeze the handle
-
Sweep from side to side
It’s also important to train workers on when to use each fire extinguisher type, since water, foam, CO₂, and dry chemical extinguishers are suited for different kinds of fires. Misusing the wrong type can make the situation worse.
Regular fire drills and training sessions contribute to the preparedness of employees, enhancing their ability to respond calmly and effectively to fire incidents.
Having robust emergency response procedures ensures that employees can react promptly and appropriately, minimizing the impact of potential accidents and contributing to a safer workplace environment.
6. Technological Advances in Lubricant Safety
Technological advances in lubricant safety have significantly improved how industries handle, use, and dispose of lubricants, enhancing workplace safety.
Here are some key technological innovations and their impact on lubricant safety precautions:
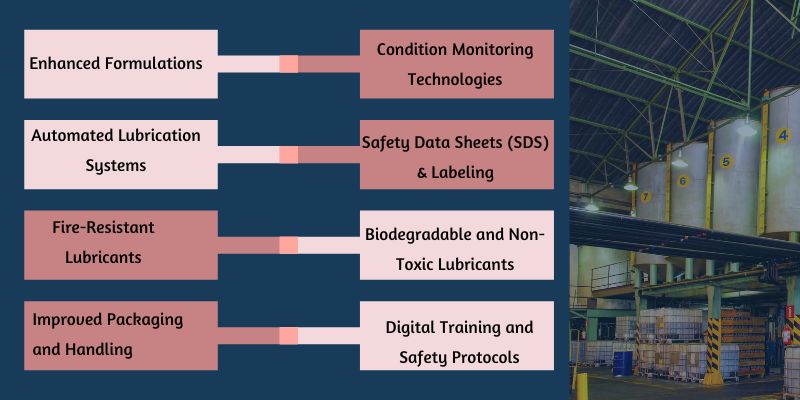
Enhanced Formulations
Modern lubricants are formulated with advanced additives that improve their performance and safety.
These additives can include anti-wear agents, corrosion inhibitors, and antioxidants that enhance the lubricant's efficiency and reduce the risk of equipment failure and accidents.
For example, lubricants with high thermal stability can prevent overheating, reducing the chances of fire hazards.
Automated Lubrication Systems

Automated lubrication systems are designed to dispense the right amount of lubricant at the right time, minimizing human error.
These systems ensure that machinery is consistently and adequately lubricated, reducing the risk of friction-related accidents and equipment breakdowns.
Automation also reduces the need for manual intervention, lowering the chances of exposure to hazardous substances.
Condition Monitoring Technologies
Advanced condition monitoring technologies, such as vibration analysis, infrared thermography, and oil analysis sensors, allow for real-time monitoring of lubricant health and machinery conditions.
These technologies can detect early signs of lubricant degradation or contamination, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing potential safety hazards.
Condition monitoring helps maintain a safe operating environment by identifying issues before they escalate.
Biodegradable and Non-Toxic Lubricants
Developing biodegradable and non-toxic lubricants has significantly reduced environmental and health risks associated with traditional petroleum-based lubricants.
These eco-friendly lubricants are less harmful to workers and the environment, making them safer for various applications.
In accidental spills, biodegradable lubricants pose less risk to soil and water contamination, ensuring a safer workplace and surrounding environment.
Improved Packaging and Handling
Innovations in lubricant packaging and handling have also contributed to enhanced safety.
For instance, lubricants are now available in sealed, tamper-proof containers that prevent contamination and spills.
Ergonomically designed packaging allows for easier and safer handling, reducing the risk of injuries during transportation and application.
Fire-Resistant Lubricants
Fire-resistant lubricants have become essential in industries where fire hazards are a concern. These lubricants are formulated to resist ignition and prevent the spread of fire, providing an additional layer of safety.
Fire-resistant lubricants are particularly crucial in high-temperature applications and environments with flammable materials.
Digital Training and Safety Protocols
Technological advances have also improved training and safety protocols related to lubricant handling.
Digital training modules and augmented reality (AR) applications provide workers with interactive and immersive training experiences, ensuring they are well-versed in safety procedures.
These training tools can simulate various scenarios, helping workers understand how to handle lubricants and respond effectively and safely in emergencies.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and Labeling
With advancements in digital documentation, Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are now more accessible and comprehensive. They provide detailed information about lubricants' hazards and safe handling practices.
Enhanced labeling technologies, such as QR codes and RFID tags, allow easy access to safety information, ensuring workers have the knowledge to handle lubricants safely.
Technological advances in lubricant safety have significantly improved how lubricants are formulated, monitored, handled, and disposed of, leading to safer workplace practices.
By utilizing these innovations, industries can minimize risks, protect workers, and ensure a safer and more efficient operational environment.
7. Compliance Strategies
Ensuring compliance with safety regulations and standards is critical to lubricant safety precautions. Effective compliance strategies help minimize risks associated with lubricant use and maintain a safe workplace.
Here are key strategies to enhance compliance and ensure safe lubricant handling:
Understanding Regulatory Requirements
- Stay Informed: Regularly update your knowledge of relevant local, national, and international lubricant regulations. This includes OSHA standards, European REACH regulations, and specific industry guidelines.
- Training Programs: Conduct regular training sessions for employees to ensure they know the latest regulations and understand how to comply. Training should cover the proper handling, storage, and disposal of lubricants and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Documentation and Record-Keeping
- Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Ensure that SDSs for all lubricants are up-to-date and accessible to all employees. SDSs provide critical information about the hazards, safe handling, and emergency measures related to lubricants.
- Inspection Logs: Keep detailed logs of equipment inspections, maintenance activities, and lubricant changes. Review these logs regularly to identify patterns or issues that need addressing.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure all safety practices are followed correctly. Audits help identify gaps in compliance and implement corrective actions.
Safe Storage and Handling
- Proper Storage: Store lubricants in designated areas that meet regulatory requirements. This includes using appropriate containers, properly labeling, and ensuring that storage areas are well-ventilated and free from ignition sources.
- Spill Containment: Implement spill containment measures, such as bundled pallets and kits, to address any accidental spills quickly. Ensure that employees are trained to use these measures effectively.
- Temperature Control: Store lubricants at the recommended temperatures to prevent degradation and potential hazards. Temperature control can help maintain lubricants' effectiveness and reduce the risk of fire or chemical reactions.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Provide Appropriate PPE: Ensure employees have access to and use the necessary PPE, such as gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing when handling lubricants. Proper PPE reduces the risk of exposure to hazardous substances.
- Regular Checks: Regularly inspect and replace PPE to ensure it is in good condition and provides adequate protection. Encourage employees to report any damaged or worn-out PPE immediately.
Environmental Considerations
- Eco-friendly Products: Where possible, use environmentally friendly lubricants that comply with environmental regulations. Biodegradable and non-toxic lubricants are safer for both employees and the environment.
- Disposal Procedures: Follow proper disposal procedures for used lubricants and related waste. This includes using certified waste disposal services and ensuring disposal methods comply with environmental regulations.
Emergency Preparedness
- Emergency Plans: Develop and implement emergency response plans that include procedures for dealing with lubricant spills, fires, and exposures. Ensure that all employees are trained to respond effectively to emergencies.
- First Aid Training: Provide employees with training focusing on the specific risks associated with lubricant exposure. Ensure that first aid kits are well-stocked and accessible.
Continuous Improvement
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for employees to report safety concerns or suggest improvements. Regular feedback can help identify potential issues and enhance safety practices.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review and update safety protocols and compliance strategies to reflect changes in regulations, new safety information, and technological advancements.
By implementing these compliance strategies, organizations can ensure that they meet regulatory requirements and maintain a safe working environment.
Compliance protects employees, enhances operational efficiency, and reduces the risk of legal penalties.
8. Clean-Up Procedures

Before starting the clean-up process, ensure you have the necessary personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing. Assess the spill size and type to determine the appropriate response.
Small spills can often be managed with in-house resources, while larger spills might require specialized equipment or external assistance.
Containing the Spill
Immediately contain the spill to prevent it from spreading and contaminating other areas.
Use absorbent materials like spill pads, granules, or booms specifically designed for oil and lubricant spills. Place these around the perimeter of the spill to create a barrier.
Absorbing and Removing the Spill
Once the spill is contained, begin absorbing the lubricant. Start from the outer edges and work towards the center to minimize the spread.
Use absorbent pads or materials to soak up the lubricant. Replace saturated absorbents with fresh ones until all the lubricant is absorbed.
Cleaning the Affected Area
After the lubricant is absorbed, clean the affected area thoroughly. Use appropriate cleaning agents that are safe for the surface and effective in removing oil residues.
Avoid using water unless the lubricant is water-soluble, as it can spread the spill further.
Disposal of Contaminated Materials
According to local and federal regulations, all contaminated materials, including used absorbents and cleaning agents, must be disposed of.
Store these materials in labeled, sealed containers to prevent further contamination. Utilize certified waste disposal services to handle hazardous waste responsibly.
Documenting the Incident
Keep detailed records of the spill incident, including the cause, the type and amount of lubricant spilled, the response actions taken, and any environmental or safety impacts.
This documentation is crucial for regulatory compliance and reviewing and improving spill response procedures.
Training and Preparedness
Regularly train employees on spill response procedures and conduct drills to ensure preparedness. Update spill response plans and kits as needed, ensuring they are easily accessible and well-stocked.
By following these comprehensive clean-up procedures, workplaces can effectively manage lubricant spills, minimize environmental impact, and maintain a safe working environment.
FAQs
How should I respond to a lubricant spill in the workplace?
Immediately contain the spill using spill kits, notify your supervisor, and follow your workplace's emergency procedures to clean up safely.
What are the best practices for disposing of used lubricants?
Use certified waste disposal services, follow local and federal regulations, and ensure proper labeling and storage of used lubricants until disposal.
How can I ensure compliance with OSHA and EPA regulations?
Stay updated on regulations, conduct regular training and audits, maintain proper documentation, and implement adequate safety and environmental practices.
Conclusion
Prioritizing workplace lubricant safety precautions is paramount for creating a secure and healthy work environment. The potential hazards of lubricants, including health risks, fire, and explosion dangers, necessitate a comprehensive approach to safeguarding employees and the workplace.
Implementing stringent safety measures, such as using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), proper storage and handling protocols, employee training programs, and efficient ventilation systems, forms a robust defense against lubricant-related risks.
Ensuring employees have the knowledge and tools to respond promptly to emergencies, including spills and fires, is equally crucial.
Effective emergency response procedures, such as spill containment and cleanup and organized fire response strategies, play a pivotal role in mitigating the consequences of accidents.
Regular training sessions and drills contribute to workforce preparedness, fostering a culture of safety and awareness, with a significant impact achieved through integrating online safety certifications. These certifications add a formalized dimension to the training process, ensuring that employees acquire standardized and recognized qualifications in safety practices.
By embracing workplace lubricant safety precautions, organizations not only adhere to regulatory standards but also demonstrate a commitment to the well-being of their employees.
A proactive safety approach not only prevents accidents but also enhances productivity and morale within the workplace.
In summary, integrating safety precautions into daily operations is an investment in the health, safety, and overall success of the workforce and the organization.
Through a collective commitment to safety, businesses can create a workplace where employees thrive, free from unnecessary risks and hazards.