The workplace can be a hub of activity, with various tasks and machinery that pose potential risks to our eyes.
According to the Canadian Center of Occupational Health and Safety (CCOHS), every day, approximately a thousand people in North America, 200 of them in Canada, sustain a work-related eye injury.
These injuries affect the individuals involved and affect workplace productivity and safety records.
We often take our vision for granted amidst the daily grind. That's where the significance of eye safety tips in the workplace comes into sharp focus.
This article highlights the importance of eye safety in the workplace. We'll explore the common causes of eye injuries at work so you can understand how to improve health and safety in the workplace.
By raising awareness and promoting proactive eye safety measures, we aim to ensure that your vision remains valuable throughout your career, enabling you to see clearly and work safely in any professional setting.
Understanding Workplace Eye Hazards
The human eye is incredibly delicate and vulnerable, and understanding its various hazards in different work environments is paramount for ensuring eye safety.
1. Types of Eye Hazards
Here are the common eye hazard types that can affect your eyes and vision.
- Chemicals: In workplaces with hazardous chemicals, such as laboratories or industrial settings, splashes or fumes can pose significant eye risks.
- Mechanical: In construction sites, manufacturing plants, and even offices, the risk of mechanical eye injuries from flying debris, tools, or equipment is a common concern.
- Biological: Healthcare facilities and laboratories often deal with biological agents that can cause eye infections or irritations.
- Radiation: Industries like welding or healthcare use radiation, which, if not adequately shielded, can harm the eyes.
2. Common Workplace Eye Hazards
Common workplace eye hazards can vary widely depending on the work type. However, several hazards are prevalent in many workplaces:
- Flying Objects: In construction, manufacturing, or woodworking, there's a risk of debris, wood, metal, or other materials becoming airborne and entering the eye.
- Chemical Exposure: Laboratories, chemical manufacturing, and industries working with liquids or gases can pose a threat due to chemical splashes or fumes that can irritate or damage the eyes.
- Radiation: Workers in welding, healthcare (such as X-ray technicians), or industries using lasers may face radiation exposure that can harm the eyes if protective measures aren't in place.
- Biological Hazards: In healthcare settings, laboratories, or agricultural work, exposure to infectious agents or allergenic substances can pose eye-related risks.
- Dust and Particles: Dusty environments, like construction sites or workshops, can lead to eye irritation or injuries when particles enter the eyes.
- UV Exposure: Outdoor workers, such as construction personnel or agricultural workers, may be at risk of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, which can harm the eyes over time.
- Poor Lighting: Insufficient or improperly directed lighting can strain the eyes and increase the risk of accidents.
- Machinery and Tools: Using power tools, machinery, or equipment without proper safeguards can result in eye injuries if a malfunction or accident occurs.
- Computer Screens: In office settings, prolonged exposure to computer screens can lead to eye strain and discomfort.
- Sharp Objects: In healthcare, manufacturing, or even office settings, sharp objects like needles or paper can accidentally enter the eye.
Understanding these common hazards is essential for employers and employees to protect their eyes while at work proactively.
3. Potential Consequences of Eye Injuries

Eye injuries can have severe and long-lasting consequences. Some potential outcomes of eye injuries include:
- Vision Loss: Eye injuries can result in partial or complete vision loss. The severity of the vision impairment depends on the type and extent of the injury.
- Blindness: In the worst cases, mainly if the injury is not promptly treated or if the damage is extensive, blindness can occur.
- Pain and Discomfort: Eye injuries can cause significant pain and discomfort, making it difficult for the affected person to carry out their daily activities.
- Corneal Abrasions: Foreign objects, chemicals, or mechanical trauma can scratch the cornea, leading to corneal abrasions. These can be extremely painful and may cause blurred vision.
- Chemical Burns: Chemicals that come into contact with the eye can result in chemical burns. These burns may damage the eye's surface and lead to vision problems.
- Conjunctivitis: Commonly known as pink eye, conjunctivitis can result from bacterial or viral infections. It causes redness, itching, and discharge from the eye.
- Detached Retina: Severe trauma to the eye can lead to a detached retina, which requires immediate medical attention to prevent vision loss.
- Cataracts: Certain eye injuries or long-term exposure to UV radiation can increase the risk of developing cataracts, clouding the eye's lens and causing vision problems.
- Glaucoma: Some eye injuries can damage the eye's drainage system, increasing intraocular pressure and the risk of glaucoma.
- Secondary Infections: Eye injuries can create conditions where secondary infections can occur, further complicating the healing process.
It's crucial to recognize the potential consequences of eye injuries and take proactive steps to prevent them. Proper eye protection, safe work practices, and immediate medical attention in case of an injury can significantly reduce the risk of these outcomes.
Eye Safety Tips for Specific Workplace Environments
Different workplace environments pose unique risks to eye safety, requiring specific protective measures.
In industrial settings, the focus should be on guard against physical impacts and chemical splashes through shatterproof eyewear and face shields.
Laboratories require rigorous chemical safety protocols and readily accessible eyewash stations to handle accidental exposures.
Protection from debris and dust on a construction site is essential, so workers need sturdy safety goggles and regular equipment checks.
Healthcare environments demand measures to protect against biological hazards, emphasizing appropriate PPE and strict hygiene practices.
Each environment must assess its risks and implement the appropriate eye safety measures to protect workers effectively.
Here are some tailored eye safety tips for specific workplace settings:
1. Proper Eye Protection Selection
Selecting the appropriate eye protection is critical for workplace safety. Work environments present varying eye hazards, such as chemicals, dust, projectiles, or radiation. Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields are common forms of eye protection.
Choosing eye protection that adheres to safety standards relevant to your job is essential. For instance, welding tasks necessitate shaded lenses to protect against harmful arc radiation, while chemical laboratories require goggles with tight seals to prevent chemical splashes.
Make sure your eye protection is not only adequate but also comfortable to encourage consistent use.
2. Ensuring a Proper Fit
Eye protection is only adequate if it fits correctly. Ill-fitting eyewear can allow hazards to sneak in through gaps. Your safety glasses, goggles, or face shield must provide a snug and secure fit. Adjustable straps, cushioning, and anti-fog features enhance comfort and usability.
Regularly check your eye protection stays in optimal condition and replace any damaged or worn-out equipment.
3. Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are essential, especially if your work involves potential eye strain or exposure to workplace hazards.
Eye exams can detect vision issues or conditions early on, preventing long-term damage. They also ensure that your prescription, if needed, is up to date, improving overall eye health.
4. Rest and Eye Strain Prevention
In today's digital age, many jobs involve extended screen time. The 20-20-20 rule can help alleviate eye strain. Every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to focus on something at least 20 feet away.
This practice reduces eye strain, as constantly staring at screens or performing detailed tasks can cause discomfort and visual fatigue.
5. Proper Lighting
Inadequate or poorly distributed lighting can strain your eyes and lead to visual discomfort. Ensure your workspace has adequate lighting that doesn't create glare on screens or work surfaces.
Proper lighting conditions can significantly reduce eye strain and improve overall comfort and productivity.
6. Use the 20-20-20 Rule
For jobs involving prolonged screen exposure, the 20-20-20 rule is invaluable. It breaks up screen time and relaxes your eyes, reducing the risk of digital eye strain. Practicing this rule can enhance your comfort and productivity at work.
7. Adjust Screen Settings
Optimizing your screen settings can significantly impact your eye comfort. Adjust brightness, contrast, and font size to minimize glare and strain.
Consider using blue light filters, which reduce the blue light emitted by screens known to contribute to eye fatigue.
8. Use Anti-Reflective Coatings
Anti-reflective coatings on screens and eyewear can reduce glare and enhance visual comfort. They are beneficial when working in bright or varying lighting conditions. Anti-reflective coatings also improve the clarity of your vision, making tasks more comfortable and efficient.
9. Avoid Rubbing Eyes
Rubbing your eyes, especially with unwashed hands, can introduce contaminants that lead to irritation or infection. Refusing rubbing your eyes is crucial to maintain their health and prevent discomfort.
10. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for eye health. Drinking enough water throughout the day helps maintain comfortable eye moisture and overall visual comfort. Dehydration can lead to dry eyes, which can cause irritation and discomfort.
Tailored to your workplace, these tips can help protect your eyes from hazards and maintain long-term eye health. Remember, eye safety is a shared responsibility between employers and employees, so ensure that safety measures are followed diligently.
Another aspect of ascertaining safety at the workplace is training the employees. Trained employees have a better chance of responding to workplace emergencies.
Canada Safety Training offers some of the best training courses, including the following:
- WHMIS Online Certification
- Hazard Recognition Training
- H2S Training Course
- PPE Training
- Bloodborne Pathogens Certification
- Benzene Awareness Program
- Accident Incident Investigation Training
11. Avoid Digital Eye Strain

Digital eye strain, also known as computer vision syndrome, is a common issue many workers face in today's technology-driven workplaces.
It occurs due to prolonged exposure to digital screens, including computers, tablets, and smartphones.
The symptoms of digital eye strain include dry eyes, headaches, blurred vision, and neck and shoulder pain.
Adopting effective strategies and practices is essential to mitigate these symptoms and maintain eye health.
Understanding the Causes
Digital eye strain is primarily caused by extended periods of focusing on a screen.
Unlike printed text with well-defined edges, characters on digital screens are made of tiny pixels, which can be less distinct and more complex to read. This forces the eyes to work harder, leading to strain.
Additionally, the blue light emitted by screens can contribute to eye fatigue and disrupt sleep patterns. Factors such as improper screen brightness, glare, and poor posture can exacerbate these issues.
Implementing the 20-20-20 Rule
One of the most effective strategies to avoid digital eye strain is the 20-20-20 rule. This simple yet powerful technique involves taking a 20-second break every 20 minutes to look at something 20 feet away.
This allows the eye muscles to relax and reduces the continuous strain of focusing on a close-up screen.
Setting a timer or using reminder software can help ensure this practice becomes a regular work routine.
Adjusting Screen Settings
Proper screen settings can significantly reduce eye strain.
Adjusting the screen's brightness to match the ambient lighting can minimize glare and prevent the eyes from constantly adjusting to different brightness levels.
Increasing the text size and contrast can make it easier to read without straining.
Many modern devices offer blue light filters or "night mode" settings that reduce blue light exposure, which can be particularly helpful in the evening.
Optimizing Workstation Ergonomics
Ergonomic adjustments to the workstation can also play a crucial role in preventing digital eye strain.
The screen should be about 20 to 24 inches away from the eyes, with the top at or below eye level. This setup encourages a natural downward gaze, reducing neck and shoulder strain.
An adjustable chair that supports proper posture can further alleviate physical discomfort associated with prolonged screen use.
Ensuring Proper Lighting
The lighting in the workspace can significantly impact eye comfort. Avoid placing screens in front of windows or under overhead lights that can cause glare.
Instead, position the screen so that windows are to the side.
Use adjustable blinds or curtains to control natural light. Desk lamps with adjustable brightness can provide targeted lighting that reduces glare and shadows.
Regular Eye Check-Ups
Regular eye check-ups are essential for maintaining overall eye health and catching potential issues early.
An optometrist can provide personalized advice on preventing digital eye strain, recommend appropriate corrective lenses, and suggest specific exercises to strengthen the eye muscles.
For individuals who wear glasses, lenses with anti-reflective coatings can reduce glare and improve comfort when using digital devices.
Practicing Eye Exercises
Incorporating simple eye exercises into the daily routine can help alleviate strain.
One effective exercise is to look at a distant object for a few seconds, then focus on a nearby object for a few seconds, and repeat this process several times. This exercise helps improve the flexibility of the eye muscles and reduces fatigue.
Blinking more frequently can also help keep the eyes moist and prevent dryness.
Taking Breaks and Blinking
Frequent breaks from the screen are crucial for eye health. In addition to following the 20-20-20 rule, taking longer breaks to move around, stretch, and relax the eyes can significantly reduce strain.
Blinking is another simple yet effective way to keep the eyes lubricated and comfortable.
People tend to blink less often when focusing on a screen, leading to dry eyes. Consciously making an effort to blink more can alleviate this issue.
Avoiding digital eye strain requires a combination of good habits, ergonomic adjustments, and regular eye care.
These practices protect eye health and enhance overall productivity and well-being in today's digital age.
12. Wear Chemical Splash Goggles

Chemical splash goggles are essential personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to protect the eyes from harmful substances and debris in environments where chemical exposure is risky.
These goggles provide a robust barrier against splashes, fumes, and airborne particles, safeguarding the eyes from potential injuries in various industrial, laboratory, and manufacturing settings.
Importance of Chemical Splash Goggles
- Protection from Chemical Splashes: One of the primary functions of chemical splash goggles is to shield the eyes from liquid chemicals. In many workplaces, employees handle corrosive, toxic, or irritating substances that can cause severe damage if they come into contact with the eyes. Goggles prevent these hazardous substances from reaching the eyes, thus preventing potential injuries.
- Barrier Against Fumes and Vapors: In addition to liquid splashes, many chemical processes release fumes and vapors that can be harmful if they come into contact with the eyes. Chemical splash goggles are designed to form a seal around the eyes, protecting against these airborne hazards and reducing the risk of irritation or chemical burns.
- Protection from Particulate Matter: In environments where dust or small particles are airborne, such as laboratories or industrial settings, chemical splash goggles can protect the eyes from mechanical injuries. If it comes into direct contact with the eyes, particle matter can cause abrasions, cuts, or other injuries.
Features of Chemical Splash Goggles
- Sealed Design: Unlike regular safety glasses, chemical splash goggles are designed to fit snugly around the eyes, creating a seal that prevents liquids and fine particles from entering. This seal is crucial for providing comprehensive protection in hazardous environments.
- Anti-Fog Coating: Many chemical splash goggles are equipped with an anti-fog coating to maintain clear vision during use. This feature prevents the lenses from fogging, ensuring the wearer can see even in humid or high-temperature conditions.
- Impact Resistance: Chemical splash goggles are typically made from durable materials that can withstand impacts. This feature is essential in environments where flying debris or accidental bumps are likely, providing an additional layer of eye protection.
- Comfort and Adjustability: Comfort is a crucial consideration for PPE that needs to be worn for extended periods. Chemical splash goggles often feature adjustable straps and cushioned seals to ensure a comfortable and secure fit, allowing for prolonged use without discomfort.
When to Wear Chemical Splash Goggles
- Laboratory Work: In laboratories where chemicals are routinely mixed, heated, or otherwise handled, the risk of splashes and exposure to harmful substances is high. Chemical splash goggles are essential to prevent accidental eye injuries in these settings.
- Industrial Settings: Workers in manufacturing, construction, and chemical processing industries are often exposed to hazardous substances. Chemical splash goggles provide necessary protection in these environments, especially when dealing with liquids that could splash or generate harmful fumes.
- Cleaning and Maintenance Tasks: Many cleaning and maintenance tasks involve using strong chemicals that can be harmful if they come into contact with the eyes. Goggles are necessary to protect against splashes and accidental exposure during these activities.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Chemical Splash Goggles
- Regular Inspection: Before use, inspect the goggles for any signs of damage, such as cracks or scratches on the lenses, which could compromise their protective capabilities. Ensure that the straps and seals are intact and functioning correctly.
- Cleaning: After each use, clean the goggles with mild soap and water or disinfectant to remove chemical residues. This practice helps maintain the goggles' clarity and hygiene, providing adequate protection in subsequent uses.
- Storage: Store the goggles in a clean, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Proper storage helps prevent damage and extends the lifespan of the goggles, ensuring they remain effective over time.
- Replacement: Regularly replace goggles that show signs of wear and tear or have been exposed to harsh chemicals that may have degraded their protective properties. Using damaged or compromised goggles can put the wearer at risk of injury.
13. Use Shatterproof Eyewear
Shatterproof eyewear is essential personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to protect the eyes from potential hazards that could cause serious injuries.
Unlike regular glasses, shatterproof eyewear is constructed from materials that resist breaking upon impact, providing high protection in various work environments.
This type of eyewear is crucial for anyone working in industries with a risk of flying debris, chemical splashes, or other physical impacts that could harm the eyes.
Importance of Shatterproof Eyewear
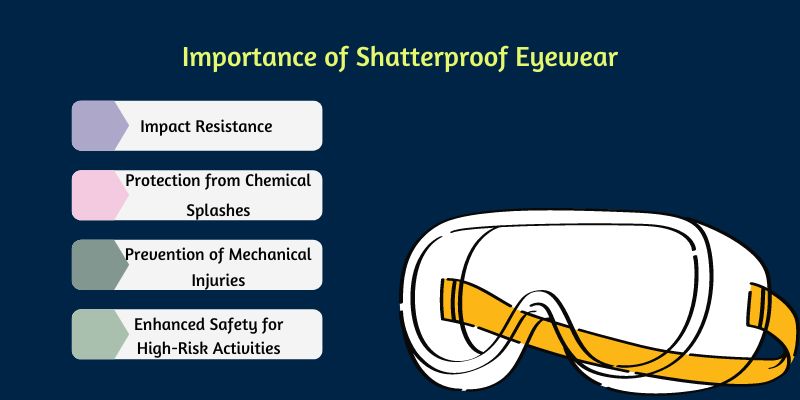
- Impact Resistance: Shatterproof eyewear is made from durable materials such as polycarbonate or Trivex, which can withstand significant impact without breaking. This feature is essential when workers are exposed to flying particles, fragments, or other projectiles that could cause eye injuries.
- Protection from Chemical Splashes: In laboratories, manufacturing, or any settings where chemicals are handled, shatterproof eyewear provides a barrier against splashes. Chemicals can cause severe eye damage, and robust protective eyewear can prevent such incidents.
- Prevention of Mechanical Injuries: Workers in construction, woodworking, metalworking, and other trades often face risks from tools and machinery. Shatterproof eyewear helps protect against debris from cutting, grinding, or drilling operations, thus reducing the risk of mechanical eye injuries.
- Enhanced Safety for High-Risk Activities: Welding, soldering, or working with power tools can pose significant risks to eye safety. Shatterproof eyewear ensures that the eyes are shielded from sparks, intense light, and sharp fragments, enhancing safety.
Features of Shatterproof Eyewear
- Material Composition: The primary materials used in shatterproof eyewear, such as polycarbonate and Trivex, are chosen for their high impact resistance and optical clarity. These lightweight and durable materials make the eyewear comfortable for prolonged use.
- Lens Coatings: Many shatterproof eyewear options include additional coatings, such as anti-scratch, anti-fog, and UV protection. These coatings enhance the functionality and durability of the eyewear, ensuring clear vision and long-lasting performance.
- Comfort and Fit: Shatterproof eyewear is designed to be comfortable, with features like adjustable nose pads, flexible frames, and secure fit mechanisms. A proper fit is crucial to ensure the eyewear stays in place during various activities and provides adequate protection.
- Versatility: Shatterproof eyewear is available in various styles and designs, including wraparound frames and models with side shields. This versatility allows users to choose the best option for their needs and preferences.
When to Use Shatterproof Eyewear
- Industrial Work: In settings such as construction sites, manufacturing plants, and workshops, the risk of eye injuries from flying debris and mechanical operations is high. Shatterproof eyewear is essential to protect workers from these hazards.
- Laboratory Settings: Researchers and technicians working with chemicals, biological agents, or hazardous materials should wear shatterproof eyewear to prevent exposure to harmful substances.
- Outdoor Activities: In environments with a risk of physical impact from environmental factors, such as forestry or landscaping, shatterproof eyewear offers protection against branches, dirt, and other debris.
- Sports and Recreational Activities: Activities like cycling, shooting, or extreme sports pose risks of eye injuries from impacts and projectiles. Shatterproof eyewear provides the necessary protection to prevent such injuries.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Shatterproof Eyewear
- Regular Inspection: Before use, inspect the eyewear for any damage, such as cracks or deep scratches, which could compromise its protective abilities. Ensure that the lenses are clear and the frames are intact.
- Cleaning: Clean the eyewear regularly with a mild soap solution and a soft cloth to remove dirt, dust, and chemical residues. Avoid using abrasive materials that could scratch the lenses.
- Storage: When not in use, store the eyewear in a protective case to prevent damage. Keep it dry, calm, and away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Replacement: Replace shatterproof eyewear that shows signs of wear and tear or has been compromised during use. Using damaged eyewear can increase the risk of injury.
14. Use Eyewash Stations
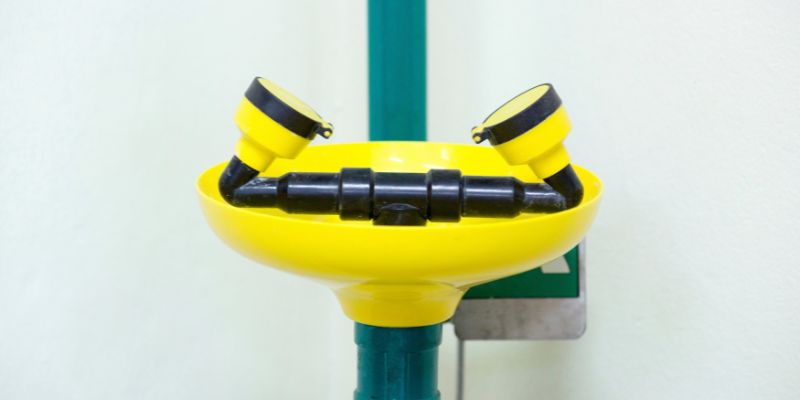

Eyewash stations are critical safety installations where employees are exposed to harmful substances or environments that pose a risk to eye health.
These stations provide a means to quickly and effectively flush contaminants from the eyes, reducing the severity of injuries and preventing long-term damage.
Having accessible and well-maintained eyewash stations is crucial to workplace safety protocols.
Importance of Eyewash Stations
- Immediate Response to Contamination: In the event of exposure to chemicals, dust, or other irritants, the ability to promptly flush the eyes with water can prevent serious injuries. Eyewash stations are designed to deliver a continuous water flow to wash away contaminants quickly and effectively.
- Reduction of Injury Severity: Rapid response to eye contamination can significantly reduce the severity of injuries. For example, flushing the eyes immediately after exposure to corrosive substances can prevent chemical burns and minimize damage.
- Compliance with Safety Regulations: Many occupational health and safety regulations, such as those enforced by OSHA, require the presence of eyewash stations in environments with a risk of eye injuries. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure the safety and well-being of employees.
- Reassurance for Employees: The availability of eyewash stations reassures employees that their safety is a priority. Knowing that measures are in place to address potential eye injuries can enhance workplace morale and safety culture.
Features of Eyewash Stations
- Consistent Water Flow: Eyewash stations are designed to provide a continuous and gentle flow of water to flush contaminants from the eyes effectively. This feature ensures thorough cleaning and prevents further irritation.
- Accessibility and Visibility: Eyewash stations are typically installed in easily accessible locations and marked with clear signage. This ensures that employees can quickly locate and use the stations in an emergency.
- Ease of Activation: Eyewash stations are designed for quick and easy activation, often with a simple push or pull mechanism. This allows for immediate use without requiring complex instructions or operations.
- Temperature Control: Some eyewash stations are equipped with features to control the temperature of the water, ensuring it is within a safe and comfortable range for use. This is important to prevent additional discomfort or injury from water that is too hot or cold.
When to Use Eyewash Stations
- Chemical Exposure: In environments where chemicals are used, such as laboratories, manufacturing plants, and cleaning operations, there is a high risk of accidental splashes or spills that can affect the eyes. Eyewash stations provide an immediate means to flush these chemicals away.
- Dust and Particulate Matter: In industrial settings where dust and other fine particles are prevalent, such as construction sites or woodworking shops, eyewash stations are essential for removing irritants from the eyes.
- Biological Hazards: Workers in healthcare, research, and sanitation industries may be exposed to biological hazards such as bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens. Eyewash stations help mitigate the risk of infection and contamination in these scenarios.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Eyewash Stations
- Regular Inspection and Testing: Eyewash stations should be inspected regularly to ensure they function correctly. This includes checking for blockages, verifying the water flow rate, and ensuring the activation mechanism works smoothly.
- Cleaning and Sanitization: Eyewash stations should be cleaned and sanitized periodically to prevent bacteria or mold growth. This helps maintain their hygiene and effectiveness.
- Training and Awareness: Employees should be trained on the proper use of eyewash stations, including how to activate them and the flushing duration required. Regular drills and informational sessions can enhance preparedness and response in an emergency.
- Clear Signage and Accessibility: Ensure eyewash stations are clearly marked and easily accessible. Remove any obstacles that could impede quick access, and ensure the stations are located where they are most needed.
Final Words
Prioritizing eye safety in the workplace is not just a matter of compliance but a fundamental commitment to the health and well-being of employees. The significance of addressing eye hazards cannot be overstated.
Eye injuries in the workplace are not only painful but often preventable through vigilance and adherence to safety guidelines. This article has shed light on eye safety tips in the workplace.
Remember, safeguarding your vision is a shared responsibility. Employers should provide suitable eye protection, offer regular training, and create a safety culture.
On the other hand, employees must actively engage in safety practices, use provided protective gear consistently, and seek medical attention promptly in case of injury.
By implementing these eye safety tips and promoting a workplace culture that values eye health, we can significantly reduce the risk of eye injuries, enhance comfort and productivity, and ensure a brighter, safer future for all workers.